The Impact of Separation of Powers in Democracy
Learn about the essential concept of separation of powers in democracy and its pivotal role in ensuring effective democratic governance.
The Essence of Democracy: Understanding the Separation of Powers in Governance and Politics
In today's dynamic world of politics, where the news cycle never seems to rest, the concept of the separation of powers plays a pivotal role in shaping democratic governance. From the latest US political news to international political developments and upcoming political events, the principle of the separation of powers remains at the heart of effective political systems. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the essence of this concept, its historical origins, and its enduring role in modern politics and governance. We will also explore its implications on political campaign strategies and its relevance in today's world.
The Origins of Separation of Powers
The concept of the separation of powers finds its roots in the Enlightenment era, with influential thinkers like John Locke and Montesquieu championing the idea. Locke's notion of the separation of powers served as a precursor to the American Revolution, influencing the framers of the United States Constitution. Montesquieu, a French political philosopher, provided a more detailed framework, emphasizing the division of government into three distinct branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial.
The Core Principles
Legislative Power: The legislative branch, typically consisting of a parliament or congress, is responsible for making and passing laws. This branch represents the voice of the people, as elected representatives debate and vote on legislation. Their role is crucial in shaping the governance and policies of a nation.
Executive Power: The executive branch, headed by the president or prime minister, is responsible for enforcing and implementing the laws created by the legislative branch. This branch manages the day-to-day affairs of the government and plays a vital role in shaping foreign and domestic policies.
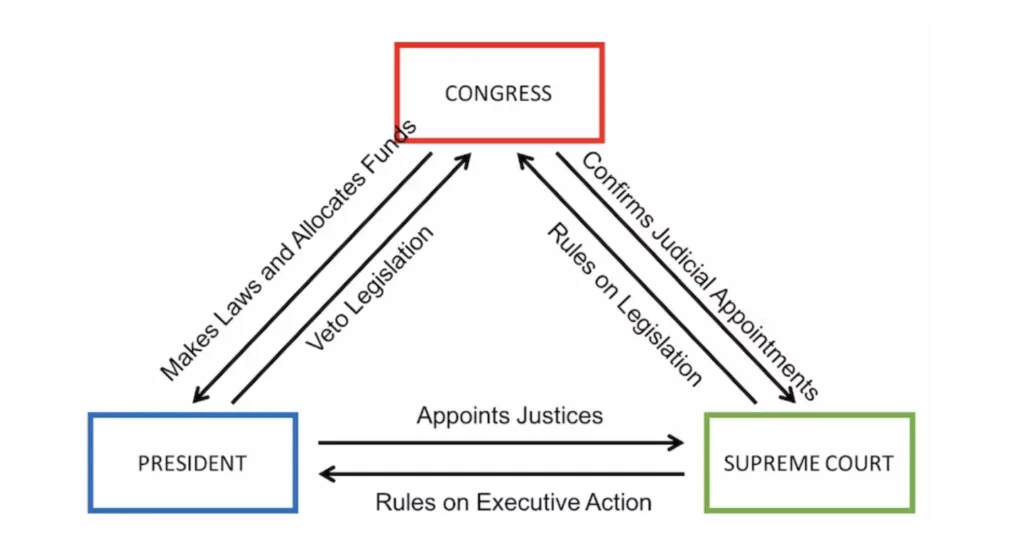
Judicial Power: The judicial branch, often embodied by a supreme court, interprets and applies the laws created by the legislative branch. It ensures that laws are consistent with the constitution and safeguards the rights and liberties of the citizens. The judiciary acts as a check on the other branches' power.
The Role of Separation of Powers in Democratic Governance
The separation of powers serves as a cornerstone of democratic governance. Its primary role is to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a single entity or branch of government. Here's how it functions:
Checks and Balances: The three branches of government act as checks on each other's powers. This prevents any single branch from becoming too dominant and potentially abusing its authority. For instance, the legislative branch can impeach the president, the executive can veto legislation, and the judiciary can declare laws unconstitutional.
Protection of Rights: The judicial branch, by interpreting and upholding the constitution, protects the rights and liberties of individuals. This ensures that the government does not infringe upon the fundamental rights of its citizens.
Accountability: Elected officials are accountable to the people through periodic elections. This accountability ensures that those in power act in the best interests of their constituents, promoting transparency and accountability in governance.
Stability and Consistency: The separation of powers provides stability and consistency in governance. Each branch has its responsibilities, preventing abrupt and unilateral changes in policy.
Relevance in Today's World of Politics
In today's fast-paced world of politics, the separation of powers remains as relevant as ever. In the US political news, we often witness the tension and balance of power among the branches of government. This dynamic ensures that no single entity can exert unchecked authority. Moreover, the principle extends beyond national borders into world politics news and international political developments, as democracies worldwide strive to maintain this delicate equilibrium.
Upcoming Political Events and Political Campaign Strategies
The separation of powers also has significant implications for upcoming political events and political campaign strategies. Politicians and political strategists must navigate the intricate system of checks and balances. They must appeal to a diverse array of constituents while respecting the limits of their branch's authority.
Campaign Messaging: Political campaigns must craft messages that resonate with the electorate while adhering to the constitution and legal framework. Understanding the role of each branch is essential in avoiding promises or proposals that might exceed a branch's powers.
Engaging with the Three Branches: Successful political campaigns involve engagement with all three branches of government. Candidates often build relationships with legislators, appeal to the executive for support, and respect the judiciary's decisions.
Influence on Policies: The separation of powers influences the development of campaign platforms and policy proposals. Candidates must consider how their initiatives align with the existing legal framework and the potential need for legislative action.
The Evolving Landscape of Separation of Powers
While the core principles of the separation of powers remain steadfast, the application and interpretation of this concept have evolved over time. In modern democratic societies, several factors have contributed to the evolving landscape of the separation of powers:
Technological Advancements: The digital age has brought new challenges and opportunities to democratic governance. Issues related to surveillance, privacy, and cybersecurity have expanded the scope of government authority and the role of the judiciary in protecting citizens' rights.
Globalization: In an era of globalization, international agreements and treaties often intersect with domestic policies. This has led to discussions on how the executive branch negotiates and implements international agreements, raising questions about the separation of powers' role in foreign policy.
Executive Orders: Presidents and heads of state have increasingly utilized executive orders to enact policy changes without congressional approval. This practice has prompted debates about the boundaries of executive authority and the need for legislative involvement.
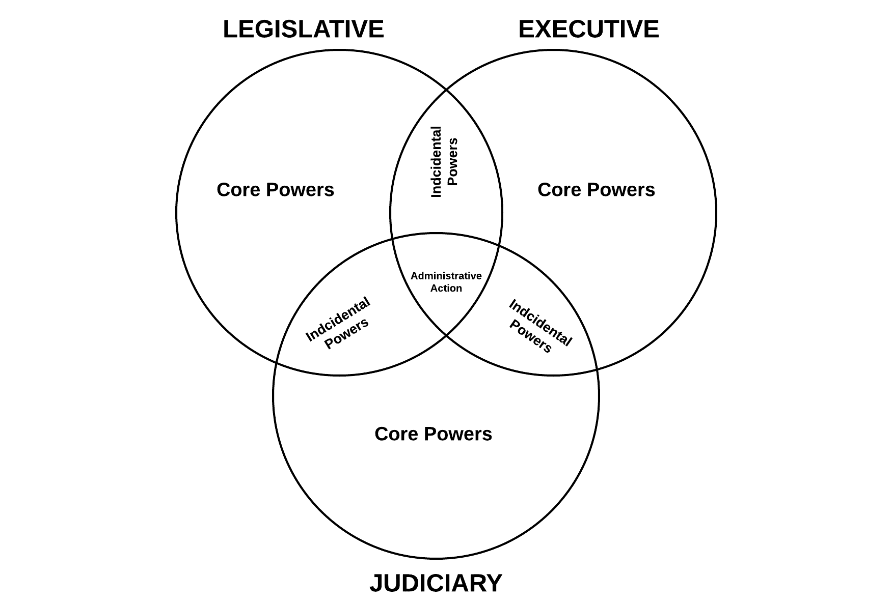
Administrative Agencies: Many modern governments rely on extensive bureaucracies and administrative agencies to implement laws and regulations. These agencies often have quasi-legislative and quasi-judicial powers, blurring the lines between branches and raising concerns about accountability.
Judicial Activism: The judiciary, tasked with interpreting laws and the constitution, sometimes engages in judicial activism, where judges actively shape policy and social issues through their rulings. This has sparked debates about the judiciary's proper role in governance.
Evolving Political Ideologies: Political ideologies and party dynamics can influence the interpretation of the separation of powers. Political leaders and parties may seek to expand or limit the powers of certain branches to advance their policy agendas.
Global Impact and Challenges
The concept of the separation of powers is not limited to any single nation; it has global implications. As seen in world politics news and international political developments, the strength and effectiveness of a nation's democratic institutions, including the separation of powers, can influence its standing on the global stage.
However, challenges persist. In some countries, authoritarian leaders have sought to undermine the separation of powers by consolidating power in the executive branch, weakening the judiciary, and limiting legislative oversight. These developments raise concerns about the erosion of democratic principles and the rule of law.
Moreover, in an interconnected world, nations often cooperate on global issues such as climate change, security, and trade. Balancing the need for international cooperation with domestic sovereignty can test the separation of powers and challenge traditional understandings of its role.
The Way Forward
In an ever-changing political landscape, the separation of powers remains a crucial safeguard for democracy and the protection of individual rights. To ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness, several steps can be taken:
Public Awareness: Educating citizens about the importance of the separation of powers and its role in democratic governance is essential. An informed electorate can hold their leaders accountable and demand the preservation of this fundamental principle.
Legislative Oversight: Legislators must actively fulfill their role in checking the executive branch. Robust congressional oversight is crucial in maintaining the balance of power.
Judicial Independence: Protecting the independence of the judiciary is vital. Judges must be free from political pressures to make impartial decisions based on the law and constitution.
Adaptation: As society evolves, democratic institutions, including the separation of powers, must adapt. This may involve updating legal frameworks to address new challenges and technologies.
International Cooperation: While safeguarding domestic sovereignty, nations should also seek ways to collaborate on global issues without compromising their democratic principles.
The concept of the separation of powers is a timeless and essential element of democratic governance. It serves as a foundational pillar, ensuring that power remains dispersed, accountable, and aligned with the best interests of the people. In a world marked by rapid change, this principle remains a beacon of stability and protection of rights. Its continued relevance, adaptation, and preservation are essential for the health and vitality of democracies worldwide. By understanding its role and actively upholding it, we can secure the future of democratic governance and politics for generations to come.
What's Your Reaction?