Methyl Vinyl Ketone (Vinyl Methyl Ketone) – A Comprehensive Guide to Butenone
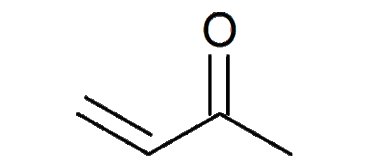
Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK), also known as vinyl methyl ketone or butenone, is a versatile organic compound that plays a critical role in chemical synthesis. With the molecular formula C4H6O, it is a colorless liquid characterized by its sharp, pungent odor.
Introduction to Methyl Vinyl Ketone (Butenone)
Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK), also known as vinyl methyl ketone or butenone, is a versatile organic compound that plays a critical role in chemical synthesis. With the molecular formula C4H6O, it is a colorless liquid characterized by its sharp, pungent odor. MVK belongs to the ketone family and has wide applications in the fields of organic synthesis, polymer production, and pharmaceutical research.
This guide provides an in-depth look at the chemical properties, production processes, applications, and safety considerations associated with methyl vinyl ketone, making it an essential resource for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Chemical Structure and Properties of Methyl Vinyl Ketone
Chemical Formula and Structure
Methyl vinyl ketone is represented by the molecular formula C4H6O. Its structure features a ketone functional group (-C=O) attached to a vinyl group (-CH=CH2). The unique combination of these groups imparts reactive characteristics that make MVK a valuable compound in various chemical reactions.
Key Properties
- Molecular Weight: 70.09 g/mol
- Boiling Point: 81.4°C
- Melting Point: -7°C
- Density: 0.840 g/mL at 25°C
- Solubility: Soluble in water, alcohol, and ether.
These properties underscore its reactivity, particularly in addition reactions and polymerizations.
Synthesis and Production of Methyl Vinyl Ketone
Methyl vinyl ketone is synthesized through various methods, depending on industrial requirements and the availability of raw materials. Key production pathways include:
1. Aldol Condensation
Aldol condensation involves the reaction of acetone with formaldehyde in the presence of a base catalyst. The intermediate compound undergoes dehydration to yield methyl vinyl ketone.
2. Oxidation of Butene
In this process, butene is oxidized using a metal catalyst, typically palladium or platinum, to produce MVK. This method is often used for large-scale industrial production.
3. Pyrolysis of Acetone Derivatives
Acetone derivatives are subjected to high-temperature pyrolysis, leading to the formation of MVK through the elimination of water molecules.
Each of these methods offers distinct advantages based on cost-effectiveness, scalability, and environmental considerations.
Applications of Methyl Vinyl Ketone
Methyl vinyl ketone Supplier versatility makes it indispensable in various industries. Here are a few of its more noteworthy uses:
1. Organic Synthesis
MVK serves as a key intermediate in organic synthesis. Its highly reactive vinyl and ketone groups allow it to participate in addition, substitution, and polymerization reactions. It is frequently utilized in the manufacturing of:
- Fine chemicals
- Pharmaceutical compounds
- Flavor and fragrance precursors
2. Polymer Industry
In the polymer industry, MVK is employed as a monomer or co-monomer in the production of specialized resins and elastomers. Its reactivity enhances the physical and chemical properties of the resulting materials.
3. Pharmaceutical Applications
Methyl vinyl ketone is instrumental in synthesizing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). It acts as a precursor for anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-cancer agents, and other therapeutics.
4. Agrochemicals
MVK plays a significant role in the development of agrochemicals, including herbicides, pesticides, and growth regulators, ensuring higher agricultural productivity.
Safety Considerations and Handling
Methyl vinyl ketone is classified as a hazardous chemical due to its toxicity and reactivity. Proper precautions are essential to ensure safe handling and storage.
1. Toxicity
MVK is highly toxic when inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. Prolonged exposure can cause irritation to the respiratory tract, eyes, and skin.
2. Flammability
Being a highly flammable liquid, MVK must be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area away from sources of ignition.
3. Protective Measures
- Wear the proper PPE, such as respirators, gloves, and goggles.
- Employ fume hoods or exhaust systems in laboratory settings.
- Follow proper disposal protocols for waste materials containing MVK.
4. Emergency Procedures
In case of spills or exposure, promptly evacuate the area and follow standard emergency response measures, including the use of spill containment kits and seeking medical attention if necessary.
Environmental Impact of Methyl Vinyl Ketone
While MVK offers numerous industrial benefits, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. When released into the environment, MVK can:
- Contribute to air pollution through the formation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Affect aquatic ecosystems if improperly disposed of in water bodies.
Adopting green chemistry principles and implementing strict waste management practices can mitigate these effects.
Conclusion
Methyl vinyl ketone, or vinyl methyl ketone, is a critical compound with extensive applications in organic synthesis, polymer manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Its reactive properties, coupled with its versatility, make it an indispensable tool for researchers and industry professionals. Sulfur trioxide pyridine, also known as pyridine sulfonic anhydride, is a powerful sulfonating agent used in organic synthesis.
What's Your Reaction?